Manufacturing is an ages old topic, spanning the entire history of modern man & Cutting Process is recurring theme in man’s & Automatic manufacturing techniques.
What is cutting Process:- Separating materials is done by physically breaking bonds, or more recently by Melting by using Cutting Tools. Cutting techniques have found particular favor with sheets of material, such as metal plates, metal sheets, fabrics, etc.What is cutting Process:-Separating materials is done by physically breaking bonds, or more recently by Melting by using Cutting Tools. Cutting techniques have found particular favor with sheets of material, such as metal plates, metal sheets, fabrics, etc.
Introduction of Cutting Tools: – Cutting tool is a device used to remove unwanted material from the given work piece.
Characteristics of cutting tools:-
- work piece and it should have hot hardness i.e. the ability of material to retain hardness at elevated temperatures.
- The coefficient of friction at the tool chip interface should be low for better surface finish and less wear.
- The material should have wear resistance to prevent wear and tear of the cutting tool surface.
- It should be chemically stable so that it does not react with the work piece and chemically inert so that there is no oxidation and hence no scales and pits are formed on the surface.
- The material must have sufficient strength and toughness to withstand shocks and vibrations.
- The thermal conductivity should be high so that there is heat dissipation which is generated during the machining process thereby increasing the life of the cutting tool.
The Mechanism of Cutting Tools:-
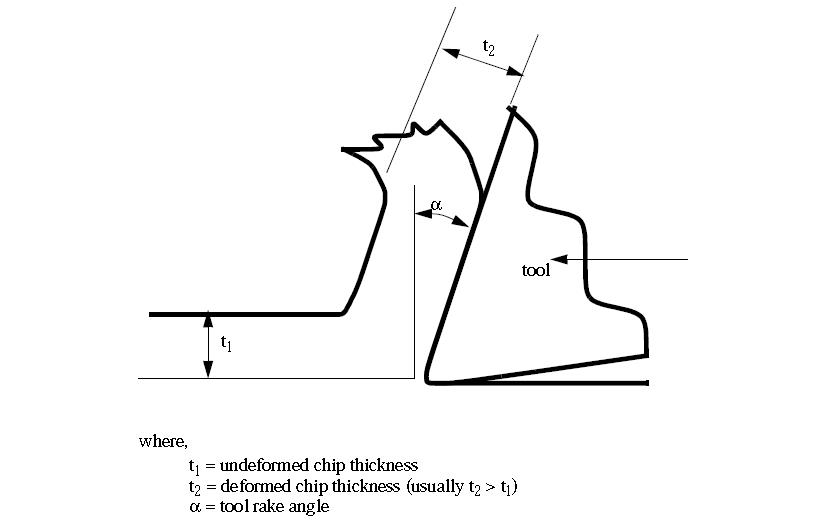
- Orthogonal Cutting – assumes that the cutting edge of the tool is set in a position that is perpendicular to the direction of relative work or tool motion. This allows us to deal with forces that act only in one plane.
- We can obtain orthogonal cutting by turning a thin walled tube, and setting the lath bit cutting edge perpendicular to the tube axis.
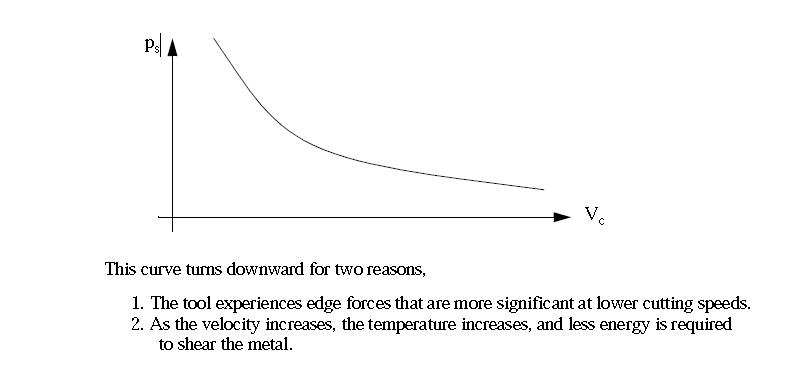
- Next, we can begin to consider cutting forces, chip thicknesses, etc.
Operations by Cutting Tools:-
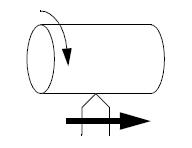
Turning – produces a smooth and straight outside radius on a part. The tool needs to overhang its holder a bit to ensure that the holder can clear the rotating work piece. Once the cutting starts, the tool and work pieces are normally in contact till the tool and work piece stay in contact till the surface gets generated.
Threading – The cutting tool is moved quickly cutting threads. The process of thread milling provides reliability because of production of short chips. It has the ability to adjust size/tolerance and full thread to the bottom of a hole.
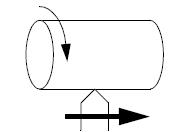
Facing – The end of the part is turned to be square. Facing is the process for metal removal from the end of a work piece for creating a flat surface. When a lathe cutting tool is used for metal removal metal, it applies a considerable tangential force to the work piece.
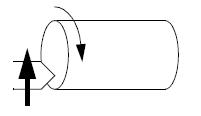
Tapering – the tool is moves so as to cut a taper (cone shape). A conical surface is created by gradual reduction or increase in diameter from a cylindrical work piece. The tapering operation is suitable for usage in construction of machines.
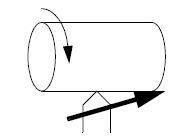
Parting/Slotting/Grooving – A tool is moved in/out of the work. Shallow cut will leave a formed cut; a deep cut will cut off the unsupported part. This is grooving or recessing operations are usually done on workpiece should to make sure that mating parts have a correct fit.
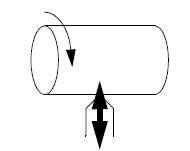
Drilling/Boring – A cutter or drill bit is pushed into the end to create an internal feature. The combined cutting & extrusion of metal is done by the chisel edge based in the drill’s centre. The high-thrust force is caused by the feeding motion first extrudes metal under chisel edge.
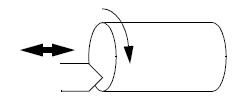
Tool Bits & Inserts: – A tool bit is a non-rotating cutting tool used in metal lathes, planers & shapers. Most high-quality cutting tools used are indexable inserts and operate at extremely high-speed.
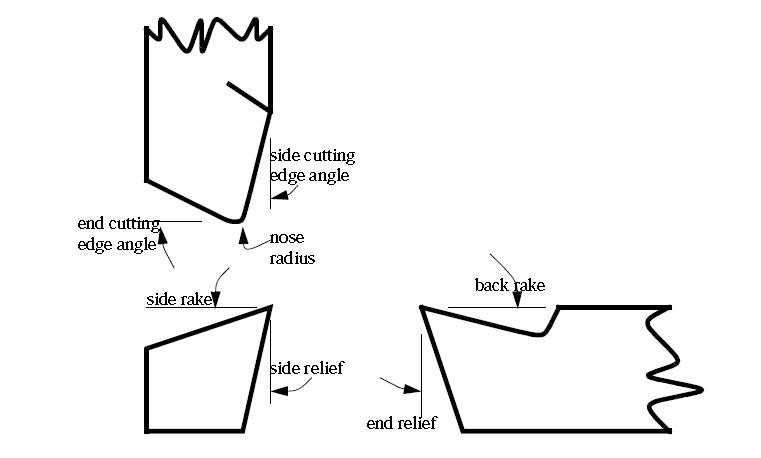
Special Cutting Tools:- Cutting tools are often designed with inserts or replaceable tips (tipped tools). In these, the cutting edge consists of a separate piece of material, brazed, welded or clamped on to the tool body. Common materials for tips include cemented carbide, polycrystalline diamond, and cubic boron nitride. Tools using inserts include milling cutters(end mills, fly cutters), tool bits, and saw blades.
Types of Special Cutting Tools:-
• Pocketed or “Index able” tools
• Carbide-tipped (TCT) or “brazed” tools
• Special thread mills
• Gang set/large radius – blended milling cutters
• Modified standards
• Solid carbide round tools
• High-speed steel round tools
• Special cartridges
• Special inserts – special TCT or HSS serrated blades
Some Common Brands of Special Cutting Tools:-

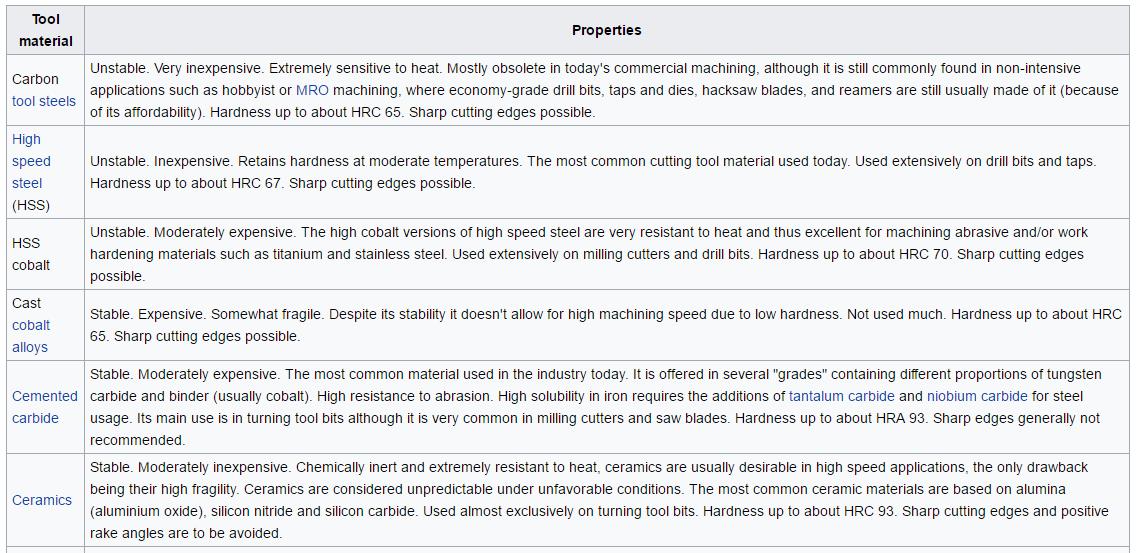
Special Cutting Tools for steel machining: –
The tools which are primarily used for machining purposes have excellent cutting ability. They are tough and have high thermal conductivity. When using these machines, it is necessary to ensure that there is no dwell or rubbing created by machine vibration or tool chatter. The machines used need to be strong enough to make deep cuts without causing a slowdown in surface set speed.

Special Cutting Tools for stainless steel machining:- The tools used for steel machining can be easily fabricated. They have high hardness temperature and should not be exposed to too much of vibration in machine bed, drive and gear boxes. Large overhangs of tool shanks of tool box need to be avoided. The distance between toolbox support & cutting tip need to be as short as possible.

Special Cutting Tools for cast iron machining: – The cutting tools used for cast iron machining have a high level of strength and high fracture toughness. While selecting cutting tools of this type, it is essential to measure toughness of material to be machined. Users also need to check a machine’s capability both at high speeds and feed rates.

Special Cutting Tools for the machining of non-ferrous metals:- Whether inserts or solid carbide tools – our cutting materials are distinguished by maximum tool life and process security. In order to be able to achieve efficient machining results, the cutting materials have to be optimized to the application and suitable for the material to be worked.

Substrate:- Our cutting materials are composed of carbide that consists of the hard material, tungsten carbide, and a metal binder, cobalt. Typically, the tungsten carbide grains are from one half to several micrometers (μm) across and the cobalt fills the space in between. Depending on the composition and structure of the substrate, the cutting material will exhibit differing properties, which in turn have a direct impact on machining performance: the cobalt content and grain size determine hardness (= wear resistance), transverse rupture strength, or toughness:

According to the particular application, we also offer cutting tools made of cermet, a carbide based on Tic instead of WC and the binder Ni or Co. High hardness and heat resistance, a low tendency to adhesion, and a high chemical resistance set this material apart.
A particular guarantee worldwide for the quality of our cutting materials is our control and further development of the whole process: it begins with determining the composition of the powder, followed by preparing the powder, forming, sintering, grinding and coating all the way through to refining the surfaces.
Coating:- Over 80% of our tools and inserts are coated using PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) methods in order to achieve an even higher wear resistance.
Over 40 years of know-how make us a pioneer in coating technology: in 1972, CERATIZIT introduced the world’s first CVD multi-layer coating, which was called Gold Master – and became a sensation in the cutting tool industry.

A recent milestone is our extremely successful and innovative coating, COLORSTARTM: our inserts lasts up to twice as long in a variety of applications with this new type of coating. Success factors include, above all, high resistance to heat and a high toughness, which leads to stable cutting edges with minimal edge chipping.
Under the coloured coating, there is an innovative production technology: COLORSTARTM is composed of a multi-layered structure that has fine crystals, improving the mechanical properties. Another advantage is the reduced roughness of the layers, allowing the chips to be better evacuated. The newly developed layering structure, in combination with the newest of coating technologies, makes the insert appear green and red.
Criticality & Awareness of Cutting Tools:-
• In each assembly line you simply can’t ignore the power attributes of Cutting tools.
• Productivity & Quality is higher depending upon Cutting Tools.
• Buyer Should Take major precaution on while purchase this critical product.(Trial)
• Any Failure can cause idle condition in entire production home.
• This can be occurred once the % value of carbon will vary along with simultaneously element whether AL, Bo Etc. Vice versa is also applicable.
• End User needs to go for trial with proper technical back up to avoids any kind of irregularity of failure. In these trials few protocols are mandatory.
• Composition of carbon must be appropriate as per spindle speed (rpm)
• Composition of extra element apart from carbon must be appropriate as per feed speed.
• Entire trial report must be unbiased and individuality must be mentioned as per application. Example- Feed per tooth (IPT) x Number of teeth= Cutting feed (IPR).
• Dependability on work piece must be compulsory.
• Non Ferrous (N)
• Stainless (M)
• Hi Temp Alloy (S)
• Steels (P)
• Hardened (H)
• Cast Iron (K)
Therefore, to achieve a high level of perfection in workshop & industry based applications, the usage of cutting tools is a must. They can prove to be a vital asset in the tool kit of every technician and enhance the user’s proficiency manifold.



